June 2025 — Prom-nasos.com.ua
June 17, 2025
Pumping carbon dioxide with a multi-stage pump
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) – a colorless gas (under normal conditions), easily soluble in water.
In addition to the widely known fact that it is an important element of the photosynthesis process, this substance is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, agricultural, and mechanical engineering industries, among others.
In the technological process of carbon dioxide production, transportation means are essential, namely a pump unit. Carbon dioxide is in a liquid state at low temperature and high pressure.
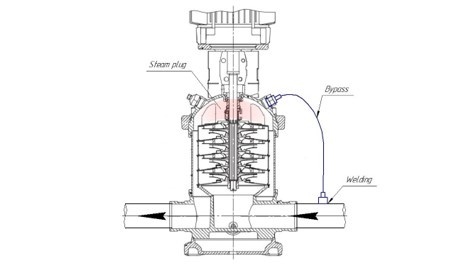
In the photo below – a vertical multistage pump installed in the carbon dioxide production line. Frost (frozen water vapor contained in the air) is observed on the pump surface and shut-off valve .
The feature of this type of pumps is the ability to generate high pressure due to the number of impellers located on a single shaft one after another. This design allows achieving significant pressures (from 3 to 25 bar).
The disadvantage of vertical configuration is the danger of forming steam-air "plugs" in the upper part of the pump due to high liquid velocity and, consequently, local boiling of carbon dioxide.
It is in this part of the pump that the mechanical seal is located. This element prevents liquid leakage from the working chamber and should be cooled by the pumped liquid, but since a steam-air zone is formed where the seal operates without liquid – "dry running", the service life of the mechanical seal is significantly reduced.
In the case of "dry running", rapid wear of friction pairs and melting of rubber rings occurs.
To eliminate this problem, a bypass tube can be used. This pump piping element allows directing vapors to the suction line, thereby preventing the formation of a steam-air "pocket" in the mechanical seal area.
June 16, 2025
Manual barrel pumps

Manual barrel pumps are the optimal solution for small enterprises, car service stations, food production facilities—anytime there is a need for product dispensing or drawing a small amount of liquid for a specific technological process.
These pumps can be used for dispensing from large containers of automotive oil, vegetable oil, fertilizers, enzyme preparations, plant protection agents, antifreeze, glycol, alcohol, diesel fuel, gasoline, and more.
Our range of manual barrel pumps is represented by the Italian manufacturer FLUIMAC.
The “yellow” pump, model N-04, is designed for working with fuels, lubricants, and fat-based products.
The pump's construction is simple and reliable. The extendable rod allows use in containers of various depths, and the FKM rubber seal ensures chemical resistance and long service life.
The “blue” pump, model N-04 Blue, has a similar design, except it uses PTE rubber seals, allowing it to handle acid solutions, vinegar, adipic acid, and other chemically active substances.
The pump delivers 0.3 L per handle stroke, with a ¾ inch connection.
The telescopic suction tube is adjustable from 500 to 950 mm and has a diameter of 34 mm.

In general, for high-viscosity products, pump types such as impeller , lobe , gear , and diaphragm are commonly used — these are primarily positive displacement pumps.
For a number of products such as oil, transformer oil, a mixture of water and flour in a 1:4 ratio, beer wort, mash, and similar liquids, a centrifugal pump with an open or wide impeller can be successfully used.
An important aspect when using such a pump with the above-mentioned products is the need to rinse the pump chamber after the pumping process is complete.
This type of pump is equipped with a mechanical seal , which generally does not require maintenance during operation. However, if the pumped product is prone to crystallization, sticking, or clumping, this may cause damage to the seal.
The photo below shows damage to the rubber bellows of the mechanical seal.
This occurred due to a failure to rinse the pump chamber in time. As a result, the friction surfaces were "glued" together by a starchy mixture, and when the pump was restarted, the rubber bellows tore.
As a result, the product began to leak from the working chamber into the space between the pump support and the electric motor.
In this case, the operator noticed the leak in time, and the mechanical seal was replaced. Otherwise, prolonged leakage could have caused damage to the electric motor, leading to significantly higher repair costs and delays in the technological process.
Our company not only sells pumping equipment and spare parts but also provides qualified selection and maintenance recommendations.
June 10, 2025
Advantages and disadvantages of wet rotor pumps
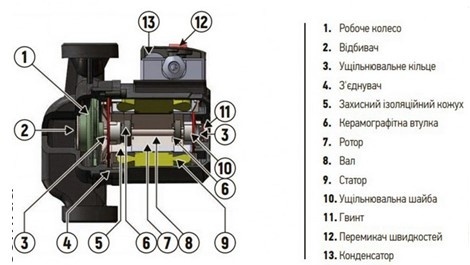
Pumps with a "wet rotor" have received their name due to the design feature – the pump rotor is supported by sliding bearings and is fully immersed in water.
The main advantage of this design is its noiseless operation. Since the rotor rotates on sliding bearings and lacks a cooling fan, the pump operates very quietly. Sometimes, the rotor's rotation can only be detected using a magnetic indicator.
Another advantage of this design is the absence of seals. It is a practically hermetic pump with only a vent plug at the end.
Moreover, most pumps with a "wet rotor" are equipped with a rotor speed switch, allowing optimal adjustment of the pump to your heating system even with minor calculation errors.
Undoubtedly, in private heating systems and in thermal nodes of multi-apartment buildings, where noise level is a critical factor, these pumps are virtually irreplaceable.
However, in industrial heating systems, boiler rooms, wood drying plants, and circulation cooling systems in the food industry, this design reveals its "downsides".
Since the gap between the rotor and stator is very small (0.5–2 mm depending on the model), the water cleanliness requirements are very high. Inclusions like scale, dirt, gasket remnants, or electrode fragments from pipe repairs or valve replacements can lead to pump failure.
This type of pump has low maintainability. Typically, service centers do not perform separate repairs of the rotor or stator or replace ceramic bearings. Instead, they offer complete replacement of the pump assembly, which costs about 80% of the pump's total price.
Another significant drawback, especially for industrial pumps, is the price. Many global leaders in pump equipment, such as Wilo, Grundfos, and DAB, have discontinued models with mechanical speed switching and now offer similar models with frequency control, which can be more than twice as expensive as the "old" models.
An alternative solution for replacing discontinued European-made pumps could be single-speed "wet rotor" pumps by EDWIN or using inline pumps with a "dry rotor" featuring a standard asynchronous motor.
June 6, 2025
Purchase of solar panels

The first prototypes of solar panels were invented in the mid-19th century. Since then, they have been improved and gained popularity, but only in the past eight years have they seen massive adoption. Today, solar energy is not only a cost-effective investment but also an environmentally sound way to address ecological challenges. Solar panels reduce CO2 emissions, helping combat global warming and climate change.
Before purchasing solar panels, you need to determine the purpose: for resale or personal use. For example, if an individual installs a system to generate income, its capacity must not exceed 30 kW. For home energy supply, the system should match the consumption.
Panels vary in power and materials: monocrystalline (most common) and amorphous.
Let’s say you need 10 kW and choose 560 W panels.
Divide the total system capacity by the power of one panel.
Add 15–20% to compensate for potential losses.
10,000 W / 560 W = 17.8 panels
With 15–20% margin: 17.8 * 1.15 = 20.47 → round up to 21 panels.
So, to build a 10 kW system, you need 21 solar panels.
You can purchase these panels from us, by clicking this link .
5 posts































































































































