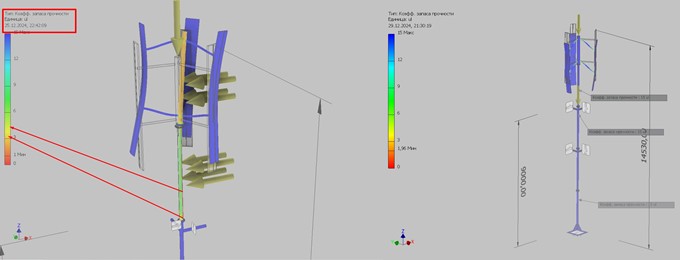
Masts for wind turbines
The installation of a wind turbine requires a mast (tower) on which it will be mounted. The height and design of the mast are calculated individually for each case.
The designs of vertical supports can vary significantly.
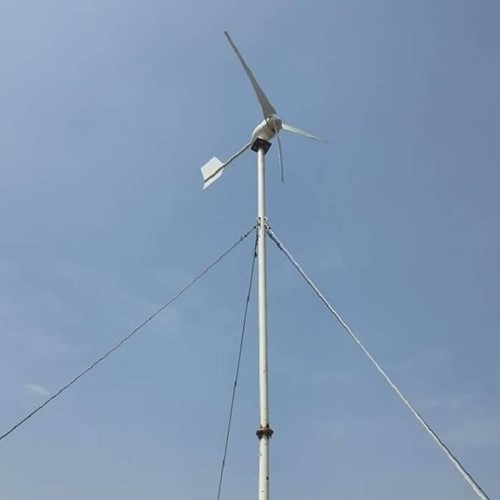
Guyed mast
This type of support is used for horizontal-axis wind turbines with a capacity of up to 10 kW.
Advantages:
- low cost due to the use of pipes and profiles with a smaller cross-section;
- possibility of installation without using a crane.
Disadvantages:
- occupies a large area, since the guy wires must be anchored around the mast at a specific angle;
- lower reliability compared to other types of supports;
- requires maintenance.

Segmented mast
The support for a wind turbine consists of several segments (pipes of different diameters). The segments are connected to each other with flanges.
This type of structure is used for installing wind turbines across a wide power range. The mast height can reach 36–40 m.
Advantages:
- high structural reliability;
- simple and fast installation;
- does not require maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- the need to use a crane to install the wind turbine;
- relatively high cost, as thick-walled pipes or profiles are used.

Monolithic conical mast
The vertical support is manufactured by welding steel strips into a hexagonal or octagonal shape.
The support is a solid conical structure with two flanges: a base flange for mounting to the foundation and a flange for mounting the wind turbine. The height of the support is limited to 12 m.
Advantages:
- high structural reliability;
- fastest installation;
- does not require maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- the need to use a crane to install the wind turbine, as well as transportation difficulties, since the support is non-dismantlable;
- relatively high cost due to the use of thick-walled pipes or profiles.

Lattice mast
This is a mast manufactured using standard structural steel sections (angle steel, square or rectangular tube, round tube, etc.).
The mast height can range from 12 to 36 m.
Advantages:
- high structural reliability;
- does not require maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- the need for welding work;
- complexity of manufacturing.

Each structure requires an individual approach and is calculated for strength, rigidity, and stability.
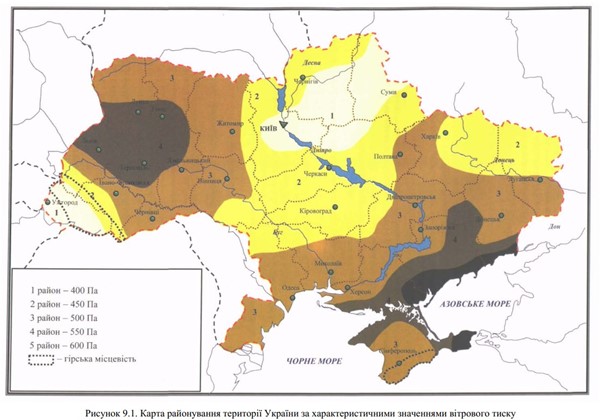
When calculating the support, the main input data are the mass of the wind turbine, the mast height, and the wind pressure in the region where the wind turbine will be installed.